|
|
Definition of Map Elements
A map usually contains the following elements:
 |
Title (and subtitle): |
 |
Legend: |
 |
Map Scale: |
 |
Credits: |
 |
Mapped Areas: |
 |
Map Symbols: Wide variety of forms and functions; the most important element of the map, along with the geographic areas rendered. |
 |
Place name and Labelling: The chief means of communicating with maps; serve to orient the reader on the map and provide important information regarding its purpose. Tips:Use the same font for the map frame, the map layout, and the map content. |
 |
North arrow: According to the rules, each map should have a north arrow. But if the map is north oriented, or if the geographical co-ordinate are already on the map the north arrow can be omitted. Tips:The north arrow must be well readable, but not be too dominant on the map. |
 |
Border and Neatlines: Both optional; borders can serve to restrain eye movements. Neatlines are finer lines than borders, drawn inside them and often intra-parallelism, rendered as part of the graticule; used mostly for decoration. |
| Graticule: Often omitted in maps today; should be included if the location information is crucial to the map purpose, e.g. into topographical maps. |
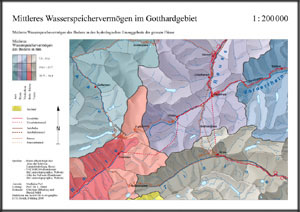
In the following example, you can observe a map which, consists of the different map elements discussed.
Since you know now all the elements that constitute a map, you have to learn how to arrange them.
On the following map, try to find out visually all the cartographic elements presented previously. This exercise is not evaluated.
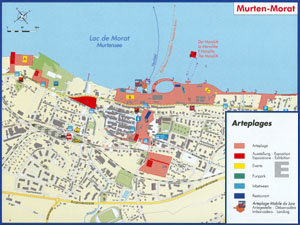 Expo 02 : Map of Morat (Expo 02)
Expo 02 : Map of Morat (Expo 02)