|
|
Input / Output of a query
A query relates to specific datasets and the data type defines whether a certain query is possible or
not. The common data types in a GIS are vector and raster and also tables. Thus, the queries on
raster data are different than the queries on vector data, although the question to be answered is
the same. The number of data sets included into the query also plays a role. The query can refer to a
single or multiple data sets. The relationships between the data involved in the query are given via
the ![]() topology (geometry) or the tables (theme). Tables can also
be related to each other. The content of the tables can be linked via key attributes. Thus, a query
can be performed over several linked tables.
topology (geometry) or the tables (theme). Tables can also
be related to each other. The content of the tables can be linked via key attributes. Thus, a query
can be performed over several linked tables.
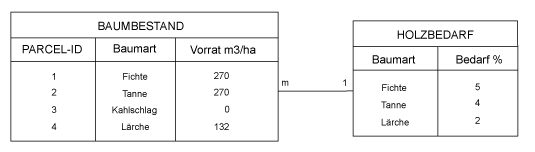 Fig. F: Linked tables
Fig. F: Linked tablesThe result of a query can be presented in different forms. The result should be presented in a form which is easy for the user to read. Normally, the results are presented as maps, tables, or figures, or in another format which allows data sharing. The following are examples of data presentation:
- Digital data transfer
- Interactive graphics on screen
- Tables, reports, and similar representations
- Passive graphics in form of maps
Some examples
| Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Inputs | Query | Type | Res. table | Res. graphic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
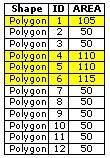
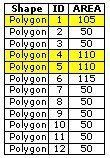
Find the buildings, which have an area of more than 100m2. | THEM |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
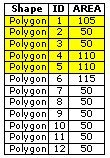
Find the buildings, which have an area of more than 100m2 and which are within a distance of 100m to Adelriver. | GEOM + THEM |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
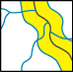
Find the buildings, which are completely within the forest. | TOPO |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
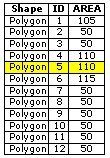
Find the area, which is within a distance of 100 m to Adelriver. | GEOM |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Find the building, which is closest to Adelriver. | GEOM |
 |
 |
Exercise
What does the spatial information in a GIS mainly consist of?
