|
|
Query classification
The aim of spatial selection and analysis is to determine spatial relationships between one or more subjects in order to locate those elements in space. The results can then be used for decision‐making. Performing a query, a number of criteria have to be formulated. To do so, the following approaches are possible:
- Thematic query:
Selection of all objects which achieve the required conditions (attributes). E.g.: "Select all spruce trees." - Geometric query:
Selection of all objects which achieve the required spatial conditions. E.g.: "Select all the houses that are located less than 250 m away from the river". - Topological query:
Selection of all objects which achieve the required conditions regarding the spatial relations between the objects. For example: "Select all the buildings that are lying in zone 1".
Subquery
Queries can be performed on the entire data set or a subset of the data. Subsets are generated via
queries. A subquery is a SELECT statement that is incorporated in
a SELECT, SELECT...INTO ,
INSERT...INTO , DELETE ,
UPDATE statement or in another subquery. A subquery is
composed of three parts.
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Comparison | predicate and a comparison operator that compares the predicate with the result of the subquery. |
| Expression | An expression that is searched for in the result of the subquery. |
| SQL statement | A SELECT statement according to the usual format of the SELECT statement. It must be in parentheses. |
Example:
SELECT * FROM product WHERE product-ID IN (SELECT
product-ID FROM orders WHERE discount >= .25);
A query can be classified in two ways, based on the result:
- Direct query:
Data are accessed interactively by the user or by an application program. Thus, a subset can be extracted, while the original data remains unchanged. The selection commands can be entered in command lines or query masks. More complex queries that require multiple single line commands can be prepared as sequences of command lines (batch, macro). In order to formulate queries, there is a formal query language. Many GIS support SQL (Structured Query Language) as query language for thematic
topics (see unit "Thematic Selection").
SQL (Structured Query Language) as query language for thematic
topics (see unit "Thematic Selection"). - Manipulation:
By manipulating, new geographic information elements can be created. These new elements can be used for analysis purpose in further steps. In general, the new objects have to be previously conceptually modeled , and their data structure has to be implemented in the GIS. Some GIS can generate a minimal data structure (without thematic attributes) automatically. New information can be generated combining different objects. They can be used for further analysis.
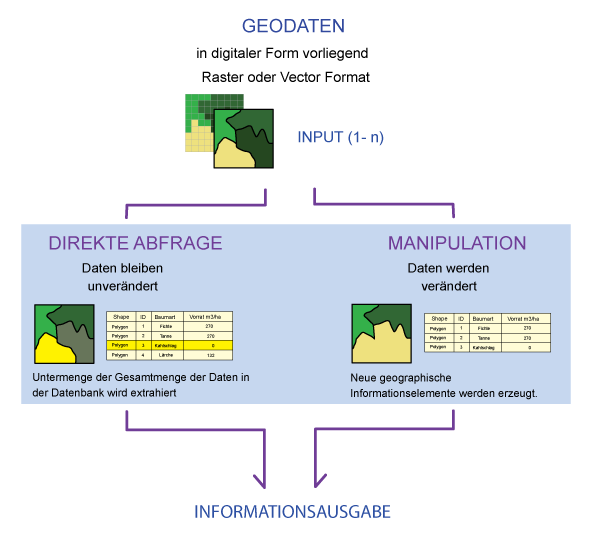 Fig. D: Classification of the query into direct query and manipulation
Fig. D: Classification of the query into direct query and manipulation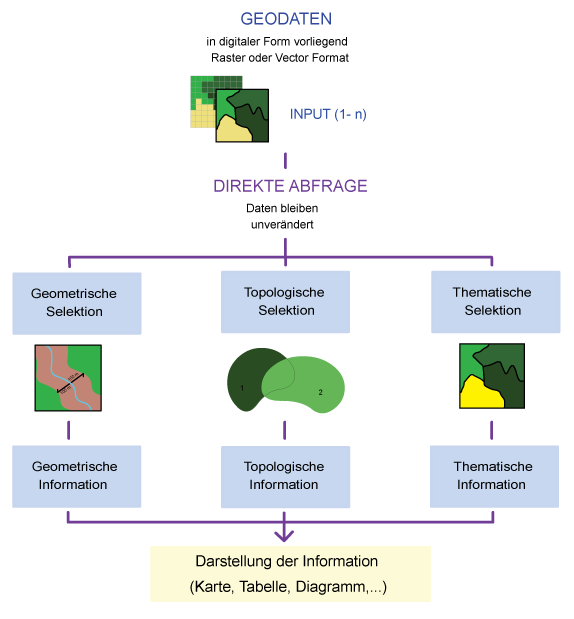 Fig. E: Splitting the direct query
Fig. E: Splitting the direct query