|
|
What are the Intentions of a Topographic Map?
A topographic map provides information on the existence, the location, and the distance between features. It also indicates variations in terrain, heights of natural features, and the extent of vegetation cover. Therefore, topographic maps have many intentions, but the first is still to give a graphic representation of a portion of the earth's surface drawn to scale. This ideal representation would be realised if every mapped feature of the area could be shown in true shape. Obviously, this is impossible: if each feature was represented in true shape, the map would result in a product impossible to read, even with a magnifying glass. This is why the map has to be generalised.
Remark: Topographic maps are often used as background information in thematic cartography.
Topographic Map versus Reality
Shown on the following example, how a topographic map provides a graphic representation of a portion of earth's surface. You will see that the main characteristics of the reality are preserved in the topographic map, and that all features are at the same level of importance (contrary to a thematic map). However, most of the features go through the generalisation process and are therefore distorted.
 Oblique aerial picture (Spiess 1993) Oblique aerial picture (Spiess 1993) |
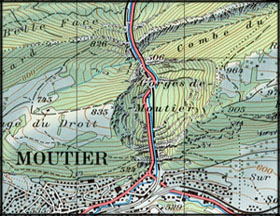 Corresponding topographic map (Spiess 1993) Corresponding topographic map (Spiess 1993) |
| Oblique aerial picture from the south of the transverse valley of Moutier. | Topographic map of the transverse valley of Moutier |
