|
|
Topological operators
Topological operators are components of spatial analysis functions of a GIS. These functions are fundamental and therefore implemented in commercial GIS, such as ArcGIS, Geomedia or MapInfo. Each system has its own formulations of spatial queries; some of them allow the user to perform topological queries using SQL. Spatial databases, such as Oracle, have been and continue to be, developed for data management purposes in GIS. Further topological operators, which are adapted to the corresponding data structure, are developed. In the following list some of the functions and the corresponding operators, provided by Geomedia, Oracle Spatial and ArcView, are shown.
| TOPOLOGICAL RELATION | ORACLE | GEOMEDIA | ARCVIEW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disjoint | disjoint | - | are within a distance of |
| Meet | touch | meet | - |
| Overlap | overlap by intersect | overlap | intersect |
| Contains | contains | entirely contains | completely contains |
| Inside | covers | are entirely contained by | contains the center of |
| Covers | inside | contain | have their center in |
| Coverered by | coveredby | are contained by | are completely within |
| Equal | equal | are spatially equal | - |
Relationships between polygons and other objects are the most frequent. Below are
some examples of topological queries:
| LAYERS | INPUT | QUERY | RESULTS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N.1 | N. 2 | Table | Graphically | ||
 |
 |
 |
Find the buildings, which lie completely within the forest. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Find the buildings, which intersect the boundary of the forest. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Find the buildings, whose centroid lies within the forest. |
 |
 |
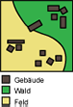
Application
As described earlier, topological queries refer to the reciprocal locations of objects in space. The
following examples illustrate this concept.
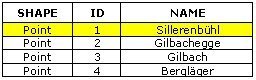
Select the huts that are reached first from the starting point (green point).
 |
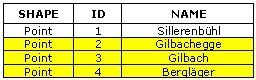
Select the huts that are in the forest (dark green area).
 |
Select the areas that touch the forest (dark green area).
 |
Which parcels are crossed by the river Allenbach?
 |
