|
|
Geometric measurement functions
Geometry is a property of an object, just as is the thematic. With the appropriate measuring functions, queries can be performed. The general geometric queries are listed below:
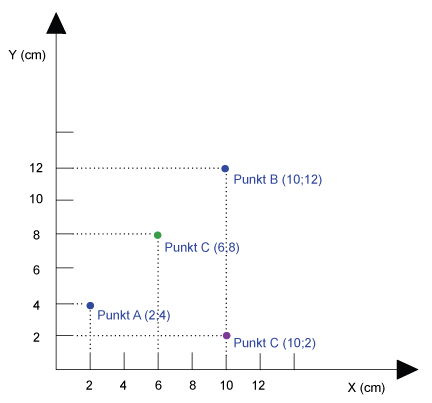
Position – where (x, y)?
Vector model
Returns the position of each point from the map as x‐ and y‐coordinates.
Raster model
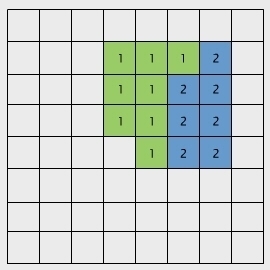 |
Example: Block encoding
|
Distance
Vector model
For vector data, the distance between two objects is calculated according to the Pythagorean Theorem and corresponds to the shortest distance.
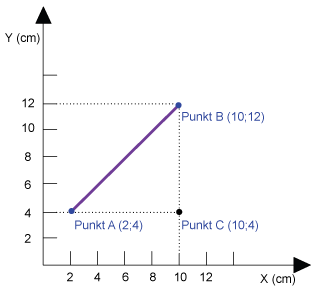 Euclidean distance Euclidean distance |
Distance between point A and B Example: The distance is 11,3 cm. |
Raster model
In the raster model, there are three different approaches to measure the distance between points.
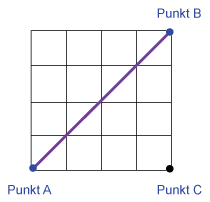 Euclidean distance Euclidean distance |
Straight line between point A and point B Beispiel: Mit einer Auflösung von 2 cm beträgt die Distanz 11,3 cm. |
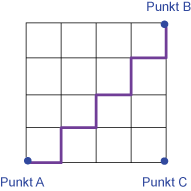 Manhattan distance Manhattan distance |
Distance along the cell boundary between points A and B. Example: Using a resolution of 2 cm, the distance is16 cm. |
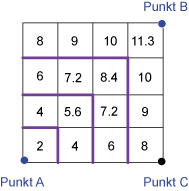 Neighborhood Neighborhood |
Concentric zones with same distance around point A. Example: Using a resolution of 2 cm, the distance is 11,3 cm. |
Practical examples
WHERE
In ArcInfo "Measuring Where" returns the x, y position
of a selected point on a map.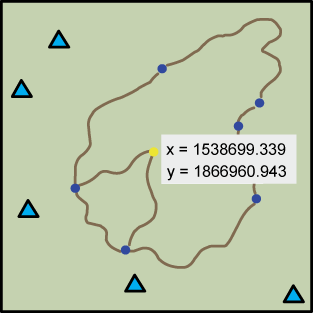
LENGTH
In ArcInfo "Length" returns the length of a line
section, which consists of two or more points. 
WITHIN A CERTAIN DISTANCE
Two objects are lying "within a certain distance" if the distance between them is smaller than the
given distance. Traditional GIS software offer pre‐programmed tools to answer these questions.
Question 1:
Select all mountain peaks that are less than 500m away
from the cabins (planimetric).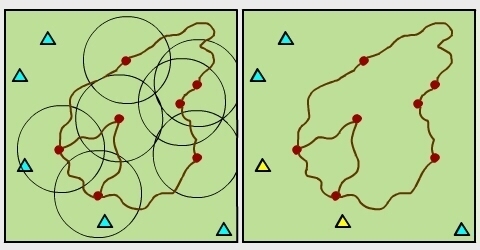
Question 2:
Select all the trees that are less than 200m away from
the collection point.
Size
Vector data model
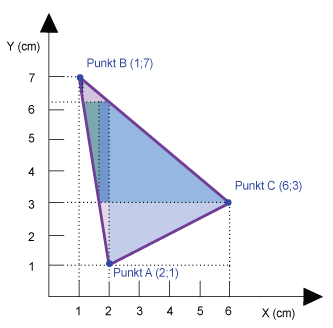 |
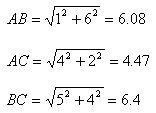 PERIMETER Sum of the length of all single sections. AREA Sum of the area of the simple geometric shapes (e.g. triangles and rectangles), into which the main object can be devided. |
Raster data model
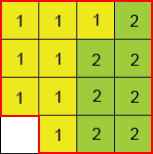 |
PERIMETER Number of cell edges, which delimit the object, multiplied by the resolution of the cells. Example: Using a cell resolution of 2cm, the perimeter is 32 cm. AREA Number of cells, which define the object, mutliplied by the area of one cell.. Example: Using a cell resolution of 2cm, the area is 60 cm2. |
Proximity analysis / buffering
Vector data model
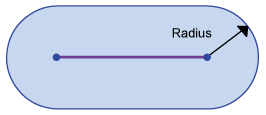
A buffer is a spatial expansion around points, lines and polygons defined by a distance.
 |
Point buffer |
 |
Line buffer |
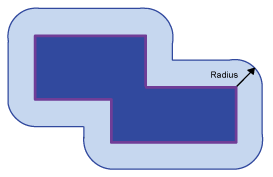 |
Polygon buffer |
Raster data model
In the raster data model, proximity is calculated for the entire raster. Then a certain distance is chosen. For in-depth look have a look at the lesson Accessibility.

Applications
Vector data model
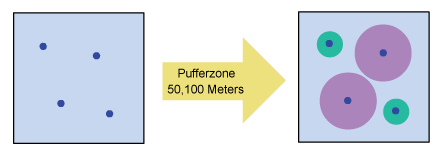
Question 1:
Canopy of trees
| Vector data model |
 |
| Raster data model |
 |
Question 2:
Calculation of the flooded area
| Vector data model |
 |
| Raster data model |
 |
Question 3:
Flooding zone of a lake
| Vector data model |
 |
| Raster data model |
 |
