|
|
Simplification
Simplification is the process which determines the important characteristics of the data, the retention of these important characteristics and the elimination of the unwanted details. When reducing a map, each map item will occupy a proportionately larger amount of space. Consequently, simplification must be practised in order to insure legibility and truthful portrayal. The elimination of unwanted map elements details (points or features) is the most often used form of simplification. The question of which individual map element will be retained and which will be eliminated is one of the most difficult tasks of simplification. The determination of which individual map elements to retain can be deduced from the purpose of the map and the place assigned to the particular data distribution in the visual hierarchy specified in the map design. This determination demands you have knowledge about the data being mapped.
Simplification of Areas
The complex house on the left is simplified as a rectangle on the
right.
Further optional information and advice for simplification of areas can be found in the following: Area_Simplification.pdf (44 Kb).
Simplification by Point Elimination
In this manually systematic elimination of points, the manipulation consists of getting rid of the points that are unimportant. A feel for this elimination process probably only comes after considerable experience.
Simplification by Point Elimination of the Outline of Pakistan.
The points indicated the map to the left, were retained on the map to the right, where they were connected with straight
line segments.
In computer-assisted cartography this simplification is less overtly subjective: point simplification is the simplification of a string of coordinate points defining a line or the outline of an area. This simplification is mostly done by a random selection of points.
Computer-assisted Point Elimination Simplification of the Outline of Sardinia.
The left simplified Sardinia map was produced by systematically retaining every 15th point in the original data file. The right one was produced by randomly selecting 1/15 of the point in the original data file.
Simplification by Feature Elimination
The simplification by feature elimination will be inconsistent if done manually. With computer-assisted feature elimination, the criteria may be the feature size, the features proximity, or a combination of both. The only thing you have to do with computer-assisted feature elimination is to specify the minimum size for retention based on output scale and line width and according to the readability rules (reference link).
Computer-assisted feature elimination simplification.
Areas on the
left map are either shown in their entirety or completely eliminated in the
feature-simplified map on the right. (Courtesy of American Congress on Surveying and
Mapping).
Smoothing/Line Simplification
Smoothing processes shift or suppress coordinates in an attempt to "plane" away small perturbations and capture only the more significant trends of the line. Many smoothing algorithms exist for computer-assisted cartography. Some of them are described in the unit Generalisation Methods. The smoothing process is often associated to displacement and classification.
Modify the smoothing degree of the road by dragging the slide-bar next to
the varying scales.
Further optional information and advice can be found in the following:
Smoothing.pdf (107 Ko).
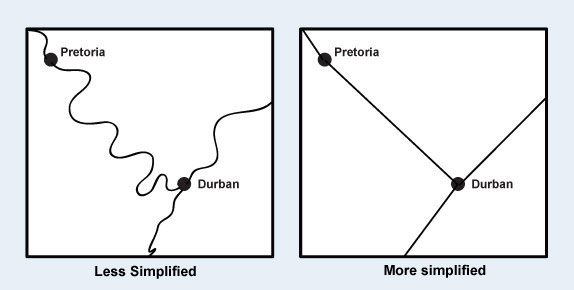
Simplification and Map Purpose
On the following example the road between the towns is straightened because
the purpose of the map is simply to show connectivity between towns, and not to
depict the road's precise location features.